Neural Volumes
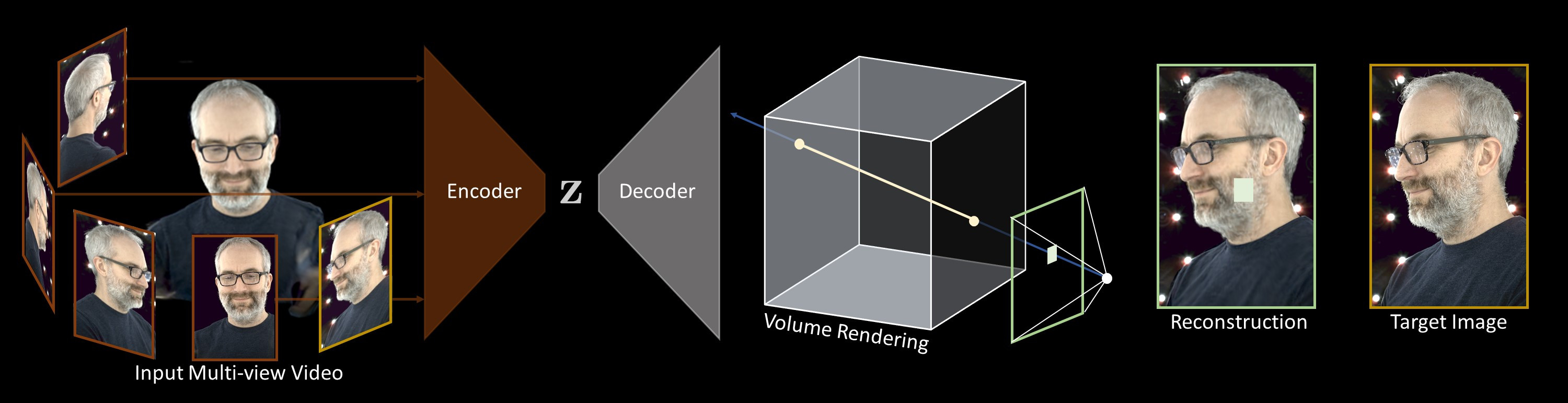
We present a learning-based approach to representing dynamic objects, supervised directly from 2D images in a multi-view capture setting. The method consists of an encoder-decoder network that transforms input images into a 3D volume representation, and a differentiable ray-marching operation that enables end-to-end training. The method learns a dynamic warp field that greatly improves the apparent resolution and reduces grid-like artifacts and jagged motion.
Read the paper
Download the code & data
Differentiable Ray Marching
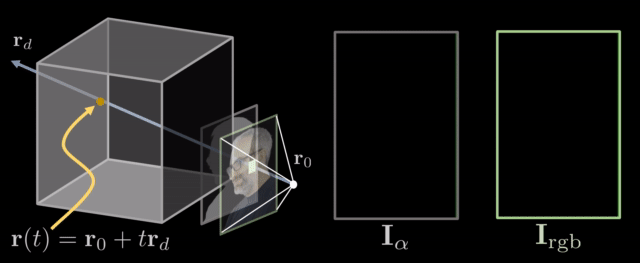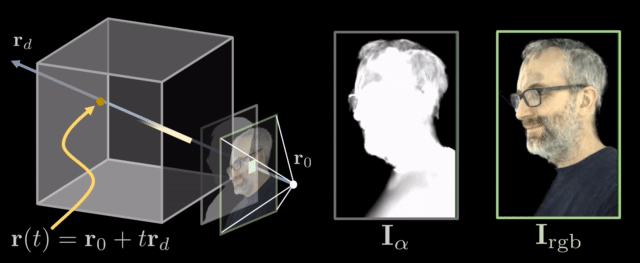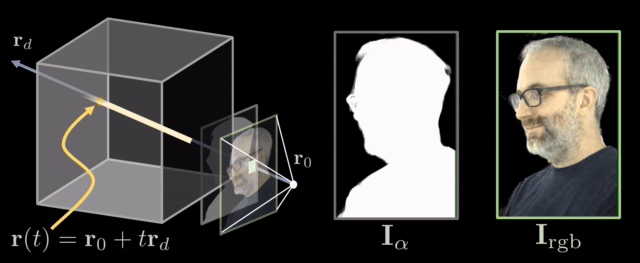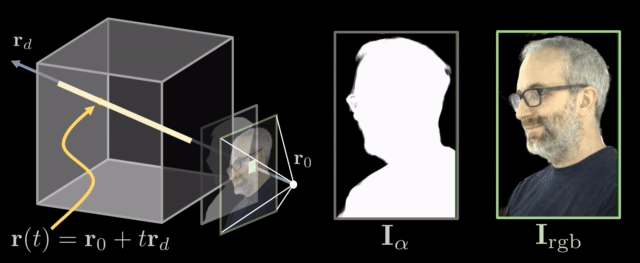
The decoder generates a volume that contains RGB and opacity values. To render this volume to an image, we use a differentiable ray marching algorithm. The idea is that we integrate the RGB and opacity values through the volume along the ray defined by each pixel.
Example Results


Bibtex
@article{Lombardi:2019,
author = {Lombardi, Stephen and Simon, Tomas and Saragih, Jason and Schwartz, Gabriel and Lehrmann, Andreas and Sheikh, Yaser},
title = {Neural Volumes: Learning Dynamic Renderable Volumes from Images},
journal = {ACM Trans. Graph.},
issue_date = {July 2019},
volume = {38},
number = {4},
month = jul,
year = {2019},
pages = {65:1--65:14},
articleno = {65},
numpages = {14},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
}